Contents
-
news
-
Health
Brain stents: Gamechanger in preventing major strokes, experts say completely safe
Brain stents help maintain blood flow to the brain by being placed in narrow spaces within a blood vessel to keep it open and help maintain blood flow. According to experts, these stents, known as intracranial stenting, are completely safe and most useful in preventing further debilitating stroke conditions. Read on to know more.
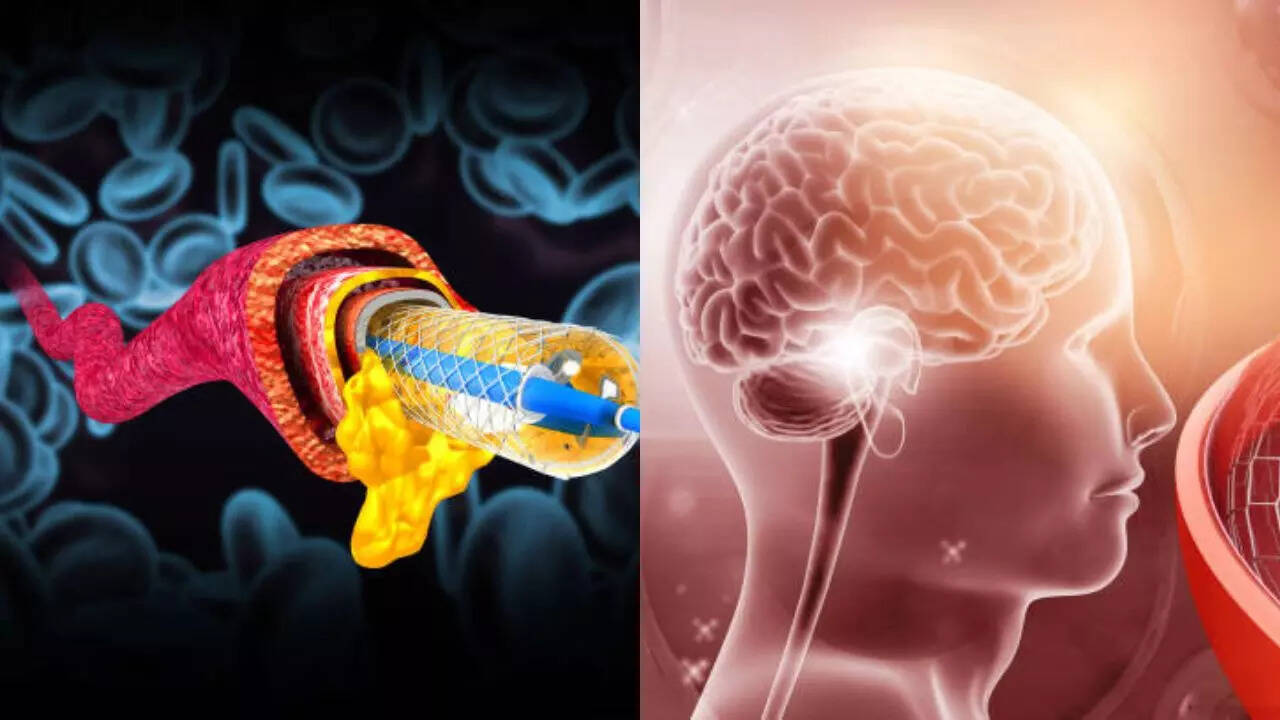
Intracranial stenting is completely safe and is most useful in preventing further debilitating stroke conditions
As soon as most people hear the word stent, they know that it is related to your heart. However, it is not widely known that stents can also be inserted into the blood vessels of the brain. According to experts, brain surgery involves intracranial stenting—opening blocked arteries in the brain to restore blood flow and help prevent debilitating strokes.
Dr Vineet Banga, director of neurology and head neurointervention at Fortis Escorts Hospital, told The Times, “These blockages for which stenting is possible can be considered equivalent to blockage of low-intermediate blood supply to the brain which can lead to stroke.” Is or can cause.” Now.
According to studies, brain stroke is the third leading cause of mortality worldwide and is about to become the top cause of disability worldwide.
Ischemic stroke, the most common form of stroke, occurs when a blockage in an artery – often from a blood clot or fatty deposits caused by atherosclerosis – disrupts blood flow to an area of the brain. Experts say only a small number of patients who experience ischemic stroke are treated with a potentially life-saving drug that can dissolve clots.
How is a brain stent placed?
According to Dr. Banga, the stent is fitted using a revascularization procedure, which uses an imaging technique called digital subtraction angiography to visualize the large blood vessels and place a balloon at the site of the blockage in the midbrain. Uses a guidewire to rotate the tipped catheter. Artery.
Once the balloon is inflated, deflated, and withdrawn, a stent is inserted to help keep the artery open. Patients with favorable outcomes three months after the procedure were able to live independently and perform normal daily activities.
“In each case, stroke, when presented to us, is usually related to blockages in the vessels supplying blood to the heart. Well, in this case, we begin to learn in detail the cause of each patient’s stroke – blockage or hemorrhage – in order to detect narrowing, given the condition in the neck – or the brain at the level of the brain. to provide the main blood supply,” he said.
“This was also ignored when explaining their aetiology – possibly exposing them to treatment with the help of stents that would open during blood vessel narrowing—strokes that would be disabling in the future,” Dr Banga said. ”
How do stents work,
When inert substance is given, Stents move along blood vessels safely The opening of the canyon above the skin or brain in urinary congestion or blood-stasis with Puta-Nelson movement pushes through a smart small prick in the leg or arm with dimples – known as neurovascular intervention. Once safely positioned, the blood supply, now open to the scalp, will be physiologically re-established, with treatment playing a role in the further-seen improvement of both.
Blood thinning medications are still important to avoid thrombus or clots forming inside the stent; Nothing too deep.
Brain stents are particularly useful for people who have had repeated strokes despite adequate medication because of severe narrowing of the blood vessels that supply blood to the brain.
Get the latest news live on Times Now with breaking news and top headlines from around the world.
How do stents work
Stents move along blood vessels safely


