Contents
-
news
-
Health
Mycoplasma pneumonia cases increase in Japan; All you need to know about respiratory tract infections
Mycoplasma pneumonia cases are increasing in Japan. There are an average of 2.84 patients per medical institution across the country. Public health officials are urging citizens to adopt preventive measures such as wearing masks, practicing hand hygiene and consulting doctors. Read on to learn more about respiratory tract infections.
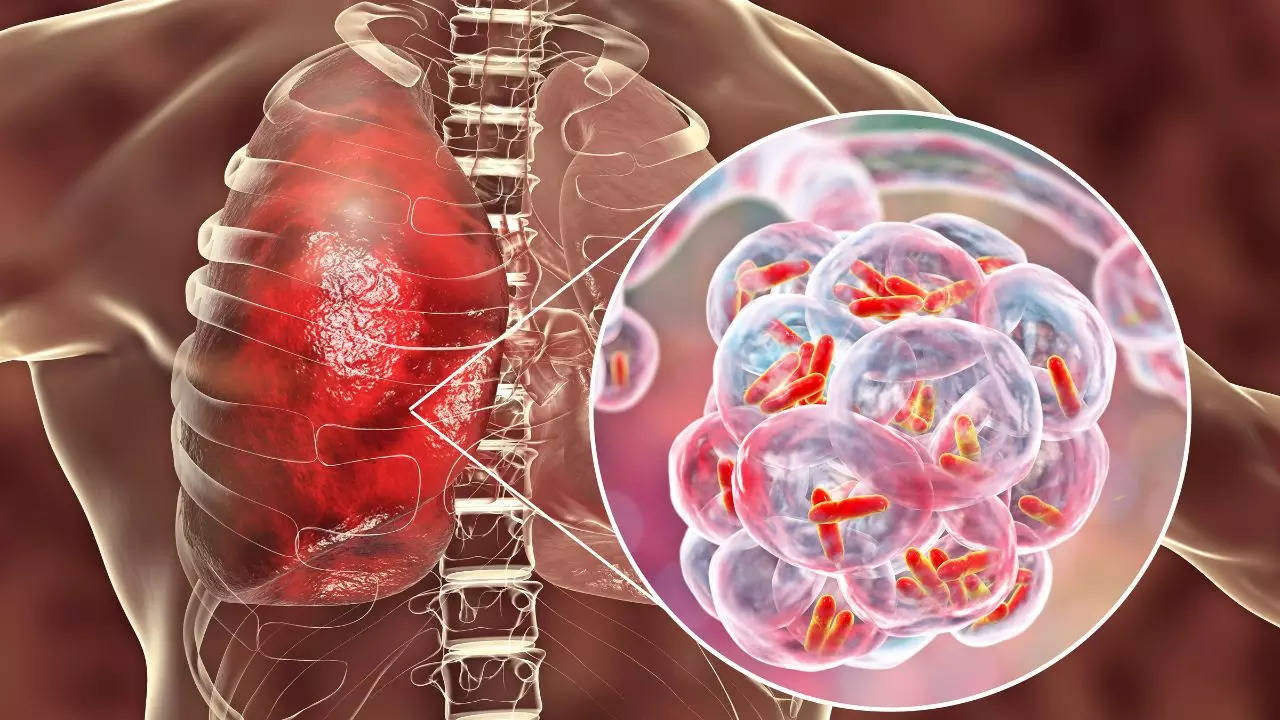
Mycoplasma pneumonia cases increase in Japan
According to Japan’s National Institute of Infectious Diseases, the country is seeing a rise mycoplasma pneumonia cases. There is an average of 2.84 patients per medical institution across the country during the week ending November 17. This represents a significant increase compared to previous weeks and is the highest figure since the current tracking system began.
Fukui Prefecture had the highest regional average of 8.83 cases per medical institution, followed by Aomori (5.0), Kyoto (4.71), and Hokkaido (4.59), Xinhua news agency reported. Major cities like Tokyo and Osaka also recorded high rates of 4.32 and 3.17 respectively.
Public health officials are urging citizens to take preventive measures, such as wearing masks, practicing hand hygiene and consulting doctors if symptoms persist.
What is Mycoplasma Pneumonia Infection?
Mycoplasma pneumoniae bacteria usually cause mild infections in the respiratory tract (parts of the body involved in breathing). Sometimes these bacteria can cause more serious lung infections that require hospital care. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says good hygiene is important to help reduce the spread of M. pneumoniae and other respiratory germs.
signs and Symptoms of Mycoplasma Pneumonia Infection
Children under 5 years of age who have M. pneumoniae infection may have different symptoms than older children and adults. Instead, they may have the following symptoms:
- sneezing
- stuffy or runny nose
- sore throat
- watery eyes
- wheezing
- vomit
- Diarrhea.
People who are at higher risk of getting infected
This infection is mostly seen in young adults and school-going children, however, it can affect anyone. Additionally, people who live and work in crowded places also have an increased risk. These are the crowded places:
- schools
- college residence hall
- military training facilities
- long term care facilities
- hospital
Other people at increased risk of serious infection are:
- People who are recovering from respiratory illness
- those who already have lung problems
- Those with weak immune systems.
Causes of Chinese Pneumonia and How It Spreads
Mycoplasma pneumoniae are bacteria that can cause disease by damaging the lining of the respiratory system (throat, lungs, trachea). People can have bacteria in their nose or throat from time to time, even without becoming sick. The CDC says that when someone infected with M. pneumoniae coughs or sneezes, they create tiny respiratory droplets that contain the bacteria. If other people breathe in those droplets they can become infected.
“Most people who spend even a short amount of time with someone with M. pneumoniae do not become infected. However, bacteria often spread between people who live together because they spend a lot of time together.
(With inputs from IANS)
Get the latest news live on Times Now with breaking news and top headlines from around the world.


