Contents
-
news
-
Health
Why Diabetic Foot Ulcers Occur and How to Prevent Them: Expert Tips to Follow
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) are a serious complication of diabetes, often arising from nerve damage or poor circulation. Common symptoms include drainage, swelling, and discoloration. We contacted a health expert who explained how it is essential to take preventive measures like blood sugar control and proper foot hygiene.
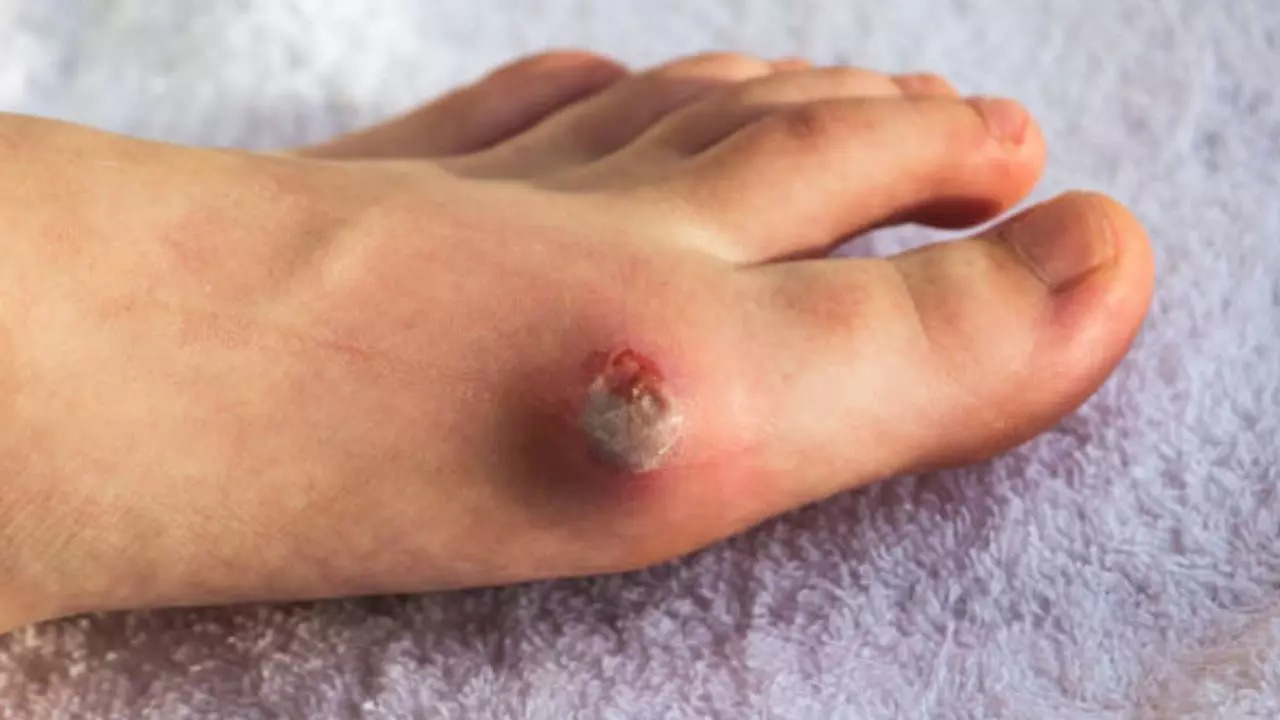
Why Diabetes Causes Foot Ulcers and How to Prevent Them: Expert Tips to Follow (Image Credit: iStock)
diabetes It is a complex condition that comes with a variety of complications that can arise from prolonged, uncontrolled blood sugar levels. is one of the most serious complications diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs), also known as diabetic foot disease (DFD) or diabetic foot syndrome (DFS). DFUs are open sores or wounds that develop primarily on the feet, often caused by nerve damage or poor circulation due to diabetes. If left untreated, these ulcers can become seriously infected.
We consulted Dr. N., a diabetic foot surgeon in the department of podiatry at the Rajiv Gandhi Cooperative Multi-Specialty Hospital in Palakkad, Kerala. Kaushik, who explains the important causes, symptoms, prevention strategies and treatment options for diabetes. To effectively prevent and manage this condition in patients.
Causes and risk factors for diabetic foot ulcers
Dr. N. Kaushik explains that diabetic foot ulcers occur when the skin tissue of the feet breaks down, exposing the underlying tissue. This often occurs in areas where the foot experiences the most pressure, such as under the big toe or heel. People who have calluses on their feet may be more likely to develop ulcers in these areas.
Although not all diabetics develop foot ulcers, those who do are often affected by several risk factors:
– Poorly fitting shoes: Wearing poorly made or improperly sized shoes can increase pressure and friction on the feet, which can lead to ulcers.
– Poor foot hygiene: Washing feet less often or drying them improperly can lead to skin damage and ulcers.
– Toenail problems: Improper trimming of toenails can cause minor injuries, which can turn into ulcers in diabetic patients.
– Decreased blood supply: Diabetics are prone to poor circulation, especially in the lower limbs, which can hinder healing.
– Obesity and smoking: Both can aggravate circulation problems, delay healing and increase the risk of ulcers.
Who is at risk: Dr. N. Kaushik explains that certain groups face a greater risk of developing foot ulcers, particularly older men with diabetes, who often have additional complicating health factors.
Diabetic foot ulcer symptoms
Diabetic foot ulcers do not always exhibit immediately obvious symptoms. They may go unnoticed until the infection begins. Dr. Kaushik has mentioned some common symptoms to pay attention to:
– Drainage from ulcers: This may stain socks or shoes and is one of the early indicators.
– Swelling and redness: Any unusual swelling or warmth in the foot may indicate an underlying problem.
– Black tissue (eschar): This black tissue around the ulcer is often a sign of poor blood supply, indicating that the ulcer may get worse without intervention.
– Odor and pain: In severe cases, ulcers may produce foul-smelling discharge and cause pain.
Causes: What Causes Foot Ulcers?
Dr. N. Kaushik explains that foot ulcers in diabetic patients can be caused by various factors:
1. Nerve damage: Over time, high blood sugar Nerve damage may occur, causing numbness or tingling in the feet. Decreased sensation means that small injuries may go unnoticed and develop into ulcers.
2. Blood circulation problems: Poor blood flow can hinder the body’s natural ability to heal. For diabetics, this slows down ulcer recovery and may lead to further complications.
3. High blood sugar levels: Elevated blood sugar impairs the healing process. Proper diabetes management is essential for ulcer prevention and treatment.
4. Foot deformities: Structural changes in the foot, such as bunions or calluses, can increase pressure on certain areas, making them prone to ulcers.
Diagnosis and treatment options
Foot ulcers require a thorough medical evaluation, including a physical examination by a health professional. Dr. Kaushik says doctors often use the Wagner Ulcer Classification System to grade the severity of ulcers on a scale of 0 to 5, which helps guide treatment. Diagnostic tests, including X-rays, may also be ordered to check if the infection has spread to the bones. Blood tests can reveal glucose levels and signs of infection.
Some common treatment options for diabetic foot ulcers include:
– Off-loading: Reducing pressure on the ulcerated area, often by avoiding standing or walking for long periods of time, can help ulcers heal.
– Special shoes: Patients may be advised to wear supportive shoes, braces, or inserts to reduce friction and prevent ulcers from worsening.
– Debridement: This process involves removing dead tissue and any foreign objects in the ulcer to promote healing.
– Medications and dressings: Antibiotics may be prescribed if an infection is present, and dressings that promote a moist healing environment may speed recovery.
Possible complications
Dr. N. Kaushik explains that if diabetic foot ulcers are not treated, they can lead to serious complications. Common issues include:
– Abscess formation: Untreated ulcers can lead to local accumulation of pus.
– Sepsis: If the infection spreads into the bloodstream, sepsis can occur, which can be life-threatening.
– Deformity and weakness: Long-term complications of uncontrolled diabetes can weaken the muscles and bones of the foot, leading to non-healing ulcers and changes in the structure of the foot.
– Gangrene: In severe cases tissue death may occur, requiring partial or complete amputation to prevent infection from spreading.
Diabetic foot ulcer prevention
Preventive measures are important for diabetic patients to reduce the risk of foot ulcers. Dr. Kaushik explains that more than half of diabetic foot ulcers become infected, making prevention even more important. Some steps to consider include:
– Manage blood sugar: It is important to consistently maintain glucose levels within a healthy range.
– Daily foot care: Washing feet regularly, drying thoroughly (especially between the toes), and moisturizing can prevent skin cracking.
– Proper care of toenails: Trimming toenails regularly or seeking professional help for foot care can reduce the risk of injury.
– Choose appropriate shoes: Wearing well-fitting, supportive shoes can prevent calluses and pressure points that lead to ulcers.
– Regular checkups with a podiatrist: Regular visits can help manage calluses, corns, and other skin problems that may contribute to ulcer formation.
Get the latest news live on Times Now with breaking news and top headlines from around the world.
diabetes


